This month we review John Carreyrou’s chilling story of the epic meltdown of a company, Theranos. We explore bad decision making, the limits of technology and the importance of strong corporate governance. The saddest thing and the reason Bad Blood hits so hard is that Theranos was a startup that seemed to have everything: a breakthrough blood analyzer, tons of funding, excellent board representation, and a smart, visionary female CEO. But underneath, it was a twisted cult of distrust with an evil leader.
Tech Themes
The limits of technology. Sometimes technology sounds too good to be true. Theranos’ Edison and miniLab blood analyzers were supposed to tell you everything you could ever want to know about your blood. But they didn’t work and never had a shot to work. Stanford professor Phyllis Gardener even told Elizabeth Holmes (Theranos’ founder/CEO) early-on that an early patch-like design of the product would never work: “[Holmes] just kind of blinked and nodded and left. It was just a 19-year-old talking who’d taken one course in microfluidics, and she thought she was gonna make something of it.” It was debunked by almost every scientist as wild fantasy even prior to its commercial use and subsequent fall from grace. There is something so human about wanting to believe there are no limits to technology. In today’s day of fake technology marketing, it’s easy for messaging to slowly take over a company if left unchecked. Think about Snap’s famous declaration, “Snap Inc. is a camera company.” or Dropbox’s S-1 mission statement: “Unleash the world’s creative energy by designing a more enlightened way of working.” These statements ignore what these businesses fundamentally do - advertising and storage. Sometimes there are massive leaps forward, like the transistor, networked computing, and the internet, but even these took many many years to push to fruition. When humans hear a compelling pitch, it is natural to want to remove those limits of technology because the result is so astounding, but we have to remain skeptical or risk another Theranos.
The reality distortion field. Elizabeth Holmes was obsessed with Steve Jobs. Mired in this deep fixation, she also managed to subscribe to one of Jobs’ interesting habits: the reality-distortion field. While we’ve discussed the reality distortion field before in relation to Jobs, Holmes seemed to take it to a new level. Jobs would demand something incredible be done and a lot of times his amazing team could come up with the solution. Holmes also believed this but failed to consider two things: fundamental biology and her team. Biology, at its core, is just not as flexible as the hardware and software that Apple was building. Jobs demanded an excellent product, Holmes demanded a biological impossibility. Beyond searching to enable a biological impossibility, which to be frank, can pop up after years of research (see CRISPR), Holmes operated the Theranos cult as a dictator, ruthlessly seeking out dissenters and punishing or firing them. While Jobs challenged his team repeatedly while being a huge asshole, the team, for the most part, stayed in tact (Phil Schiller, Tony Fadell, Jony Ive, Scott Forstall, and Eddy Cue). There were certainly those who got fired or left, but Holmes active rooting out of non-believers severely limited the chances of success at the company. The additional levels of secrecy were even extreme for a stealth technology startup. Startup founders need to drink the kool-aid sometimes, it comes with being visionary, but getting so drunk on power and image can only lead to personal and business demise as was the case with Theranos.
When startups turn bad. Tons of startups fail, but only a few turn truly malicious. Theranos was one of those few. The company tested people’s blood and gave individuals fake, untested medical results, including indicators of cancer diagnoses! Even when reviewing other major business failures and frauds - Jeff Skilling at Enron and Bernie Madoff’s Ponzi Scheme - nothing compares to Theranos. While it could be argued that Enron and Madoff’s schemes did more and broader financial hurt to society, at least they were never physically endangering individuals. The only comparisons that may be warranted are Boeing and the Fyre Festival. The brainchild of famous clown, Billy McFarland, the Fyrefest certainly endangered people by marooning them on an island with little food. Furthermore, Boeing’s incredibly incoherent internal review process which knowingly led to the production of a faulty airline software system, also endangered people - including two flights that crashed because of its system. Did Elizabeth Holmes set out to build a dangerous device, knowingly defraud investors, and endanger the public? Probably not. It was one decision after another. It was firing CFO Henry Mosley who called out fake projections; it was hiring Boies Schiller to pressure former employees; it was enlisting Sunny Balwani to “run” the company. It was what Clayton Christensen calls marginal thinking - the idea that the incremental bad decision or the incremental costs of doing something frequently outweigh the full costs of doing something. The incremental cost of firing the CFO who wouldn’t make fake numbers was simply easier than facing the difficult reality that the product sucked, and they had pushed through too much investor money to start again. When things turn bad, at startups or other businesses, a trail of marginal decision making can normally be found.
Business Themes
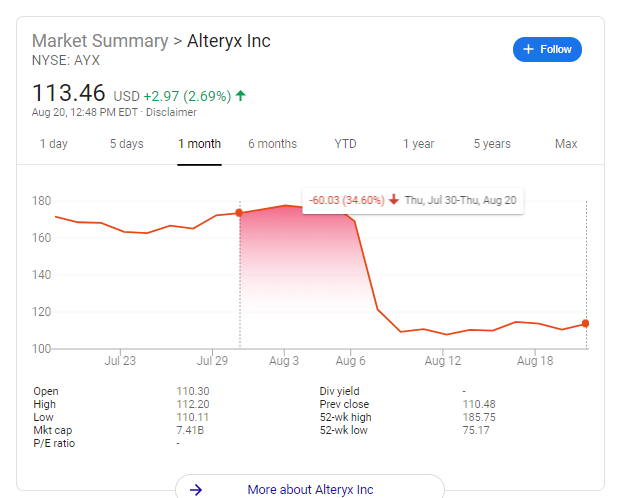
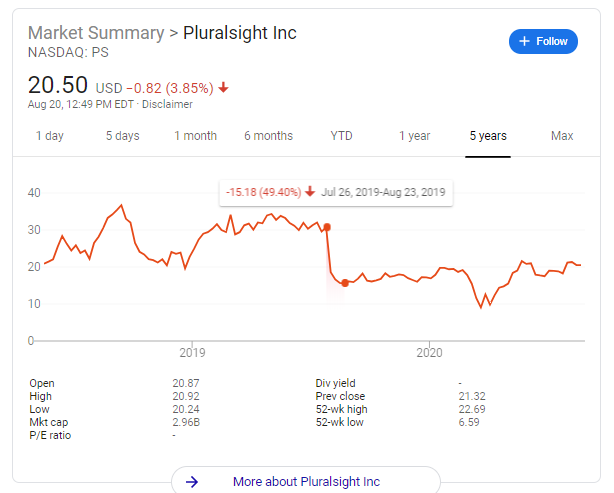
The Pressure to Succeed. Stress seems to be a part of business, but the pressure can sometimes get too big to handle. Public companies, in particular, face growth targets from wall street analysts and investors. One earnings miss or even a more modest beat than expected can completely derail a stock (See pluralsight and alteryx graphs to the right). Public company CEOs and CFOs can be fired or have compensation withheld for poor stock performance. So when a young hot biotechnology startup wanted to launch a partnership with Walgreens, Dr. J and the Walgreens team were more than ready to fast track the potential partnership. Despite not being allowed to use the bathroom, see the lab or see a partial demo of the product, Walgreens pushed through a deal so that longtime competitor, CVS, wouldn’t get the deal. As then head of the Theranos/Walgreens pilot said, "We can’t not pursue this. We can’t risk a scenario where CVS has a deal with them in six months and it ends up being real.” When the partnership was announced, even the press release sounded oddly formulaic: “Theranos’ proprietary laboratory infrastructure minimizes human error through extensive automation to produce high quality results.” There was no demo. There was no product. There was only pressure at Walgreens to beat CVS and pressure at Theranos to make something from a fake device.
The Importance of Corporate Governance. Corporate Governance has historically rarely been discussed outside of academic settings but has come into sharper focus over the past few years. Some have recently tried to bring some of the prominent corporate governance issues such as member compensation and option grants for executives to the forefront. Warren Buffet even commented on boards in his 2019 annual shareholder letter: “Director compensation has now soared to a level that inevitably makes pay a subconscious factor affecting the behavior of many non-wealthy members. Think, for a moment, of the director earning $250,000-300,000 for board meetings consuming a pleasant couple of days six or so times a year. And job security now? It’s fabulous. Board members may get politely ignored, but they seldom get fired. Instead, generous age limits – usually 70 or higher – act as the standard method for the genteel ejection of directors.” Boards are meant to help guide the company through strategic challenges, ensure the business is focused on the right things, and evaluate the CEO. Theranos’ Board of Directors was a laughable hodgepodge of old white men: George P. Shultz (former U.S. Secretary of State), William Perry (former U.S. Secretary of Defense), Henry Kissinger (former U.S. Secretary of State), Sam Nunn (former U.S. Senator), Bill Frist (former U.S. Senator and heart-transplant surgeon), Gary Roughead (Admiral, USN, retired), James Mattis (General, USMC), Richard Kovacevich (former Wells Fargo Chairman and CEO), and Riley Bechtel. The average age of the directors in 2012 was ~72 years old and few of these men could offer real strategic guidance in pursuing novel biotechnology. On top of that, as Carreyrou points out, “In December 2013, [Holmes] forced through a resolution that assigned one hundred votes to every share she owned, giving her 99.7% of the voting rights.” George Shultz even said later in a deposition, “We never took any votes at Theranos. It was pointless. Elizabeth was going to decide whatever she decided.” The episode brings more clarity to those CEOs and companies who hide behind their Board of Directors, who promise governance for investors, but rarely deliver on anything beyond pandering to the CEO’s whims. In another ludicrous comparison, Apple and Steve Jobs specifically have also been accused of shoddy corporate governance. In 2007, Apple famously backdated Jobs options, allowing him to make an instant profit, and did not even bother to report that it had issued the options. The best companies are not immune, and investors and employees should be aware of the qualifications and monetary interests of a company’s board members.
Search and Destroy. Only the Paranoid Survive, right? Wrong. There is such thing as too much paranoia. When you combine that paranoia with a manipulative persona, you get Elizabeth Holmes. It’s hard to believe that any startup or founder would need the level of security and secrecy that dominated the culture at Theranos. The list of weird security and legal gray areas include: personal security for Holmes, laboratory developed tests (instead of FDA approved tests), copious and vigorously enforced NDAs, siloed teams with no communication, and false representation in the media. Organizations are often secret and many startups operate in stealth to not give away details to competitors. Some larger companies launch new divisions in separate locations from their office, like Amazon a9. The Company hired private investigators (through its powerful law firm Boies Schiller) to threaten and track former employees including Erika Chung and Tyler Schulz. Tyler Schulz, grandson of board member George Schulz, was one of the key informants to author John Carreyrou. After he accused Elizabeth and Sunny of lying and potentially harming patients, he resigned and tried to convince his grandfather that it was all a sham. His grandfather agreed to speak with him one-on-one and at the end of the conversation surprised Tyler with two attorneys from Boies Schiller who almost forced Tyler to sign a confidentiality agreement. Tyler refused, which eventually led to the publication of Carreyrou’s first article. As early board member Avie Tevanian put it, “I had seen so many things that were bad go on. I would never expect anyone would behave the way that she behaved as a CEO. And believe me, I worked for Steve Jobs. I saw some crazy things. But Elizabeth took it to a new level.” Again, sadly, while Theranos may be the pinnacle of secrecy, paranoia and threatening behavior, eBay recently fired six employees for threatening online reviewers. On top of sending live spiders to the reviewers’ household, eBay team members would knock on their doors day or night, to scare the reviewers. How could these employees think this was ok? How could Elizabeth partake in this threatening and manipulative behavior? As Organizational Behavior professor Roderick Kramer reminds us: “‘Reality’ is not a fixed entity but rather a tissue of facts, impressions, and interpretations that can be manipulated and perverted by clever and devious businesses and governments.” Theranos’ fake Edison tests are reminiscent of Enron’s fake trading floor, where 70 low level employees once pretended to be busy to impress wall street analysts. Paranoia and secrecy are powerful weapons when left unchecked, and clearly Theranos' wielded those weapons to the fullest extent.