This month we review a unique source of information - mysterious fund manager Nick Sleep’s investment letters. Sleep had an extremely successful run and identified several very interesting companies and characteristics of those companies which made for great investments. He was early to uncover Amazon, Costco, and others - riding their stocks into the stratosphere over the last 20 years. These letters cover the internet bubble, the 08/09 crisis, and all types of interesting businesses across the world.
Tech Themes
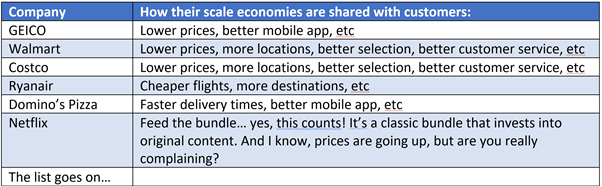
Scale Benefits Shared. Nick Sleep’s favored business model is what he calls Scale Benefits Shared. The idea is straight forward and appears across industries. Geico, Amazon, and Costco all have this business model. Its simple - companies start with low prices and spend only on the most important things. Over time as the company scales (more insured drivers, more online orders, more stores) they pass on the benefits of scale to the customer with even further lower prices. The consumer then buys more with the low-cost provider. This has a devastating effect on competition - it forces companies to exit the industry because the one sharing the scale benefits has to become hyper-efficient to continue to make the business model work. “In the case of Costco scale efficiency gains are passed back to the consumer in order to drive further revenue growth. That way customers at one of the first Costco stores (outside Seattle) benefit from the firm’s expansion (into say Ohio) as they also gain from the decline in supplier prices. This keeps the old stores growing too. The point is that having shared the cost savings, the customer reciprocates, with the result that revenues per foot of retailing space at Costco exceed that at the next highest rival (WalMart’s Sam’s Club) by about fifty percent.” Jeff Bezos was also very focused on this, his 2006 annual letter highlighted as much: “Our judgment is that relentlessly returning efficiency improvements and scale economies to customers in the form of lower prices creates a virtuous cycle that leads over the long-term to a much larger dollar amount of free cash flow, and thereby to a much more valuable Amazon.com. We have made similar judgments around Free Super Saver Shipping and Amazon Prime, both of which are expensive in the short term and – we believe – important and valuable in the long term.” So what companies today are returning scale efficiencies with customers? One recent example is Snowflake - which is a super expensive solution but is at least posturing correctly in favor of this model - the recent earnings call highlighted that they had figured out a better way to store data, resulting in a storage price decrease for customers. Fivetran’s recent cloud data warehouse comparison showed Snowflake was both cheaper and faster than competitors Redshift and Bigquery - a good spot to be in! Another example of this might be Cloudflare - they are lower cost than any other CDN in the market and have millions of free customers. Improvements made to the core security+CDN engine, threat graph, and POP locations result in better performance for all of their free users, which leads to more free users, more threats, vulnerabilities, and location/network demands - a very virtuous cycle!
The Miracle of Compound Growth & Its Obviousness. While appreciated in some circles, compounding is revered by Warren Buffett and Nick Sleep - it’s a miracle worth celebrating every day. Sleep takes this idea one step further, after discussing how the average hold period of stocks has fallen significantly over the past few decades: “The fund management industry has it that owning shares for a long time is futile as the future is unknowable and what is known is discounted. We respectfully disagree. Indeed, the evidence may suggest that investors rarely appropriately value truly great companies.” This is quite a natural phenomenon as well - when Google IPO’d in 2004 for a whopping $23bn, were investors really valuing the company appropriately? Were Visa ($18Bn valuation, largest US IPO in history) and Mastercard ($5.3Bn valuation) being valued appropriately? Even big companies like Apple in 2016 valued at $600Bn were arguably not valued appropriately. Hindsight is obvious, but the durability of compounding in great businesses is truly a myth to behold. That’s why Sleep and Zakaria wound down the partnership in 2014, opting to return LP money and only own Berkshire, Costco, and Amazon for the next decade (so far that’s been a great decision!). While frequently cited as a key investing principle, compounding in technology, experiences, art, and life are rarely discussed, maybe because they are too obvious. Examples of compounding (re-investing interest/dividends and waiting) abound: Moore’s Law, Picasso’s art training, Satya Nadella’s experience running Bing and Azure before becoming CEO, and Beatles playing clubs for years before breaking on the scene. Compounding is a universal law that applies to so much!
Information Overload. Sleep makes a very important but subtle point toward the end of his letters about the importance of reflective thinking:
BBC Interviewer: “David Attenborough, you visited the North and South Poles, you witnessed all of life in-between from the canopies of the tropical rainforest to giant earthworms in Australia, it must be true, must it not, and it is a quite staggering thought, that you have seen more of the world than anybody else who has ever lived?”
David Attenborough: “Well…I suppose so…but then on the other hand it is fairly salutary to remember that perhaps the greatest naturalist that ever lived and had more effect on our thinking than anybody, Charles Darwin, only spent four years travelling and the rest of the time thinking.”
Sleep: “Oh! David Attenborough’s modesty is delightful but notice also, if you will, the model of behaviour he observed in Charles Darwin: study intensely, go away, and really think.”
There is no doubt that the information age has ushered in a new normal for daily data flow and news. New information is constant and people have the ability to be up to date on everything, all the time. While there are benefits to an always-on world, the pace of information flow can be overwhelming and cause companies and individuals to lose sight of important strategic decisions. Bill Gates famously took a “think week” each year where he would lock himself in a cabin with no internet connection and scan over hundreds of investment proposals from Microsoft employees. A Harvard study showed that reflection can even improve job performance. Sometimes the constant data flow can be a distraction from what might be a very obvious decision given a set of circumstances. Remember to take some time to think!
Business Themes
Psychological Mistakes. Sleep touches on several different psychological problems and challenges within investing and business, including the role of Social Proof in decision making. Social proof occurs when individuals look to others to determine how to behave in a given situation. A classic example of Social Proof comes from an experiment done by Psychologist, Stanley Milgram, in which he had groups of people stare up at the sky on a crowded street corner in New York City. When five people were standing and looking up (as opposed to a single person), many more people also stopped to look up, driven by the group behavior. This principle shows up all the time in business and is a major proponent in financial bubbles. People see others making successful investments at high valuations and that drives them to do the same. It can also drive product and strategic decisions - companies launching dot-com names in the 90’s to drive their stock price up, companies launching corporate venture arms in rising markets, companies today deciding they need a down-market “product-led growth” engine. As famed investor Stan Druckenmiller notes, its hard to sit idly by while others (who may be less informed) crush certain types of investments: “I bought $6 billion worth of tech stocks, and in six weeks I had lost $3 billion in that one play. You asked me what I learned. I didn’t learn anything. I already knew that I wasn’t supposed to do that. I was just an emotional basketcase and I couldn’t help myself. So maybe I learned not to do it again, but I already knew that.”
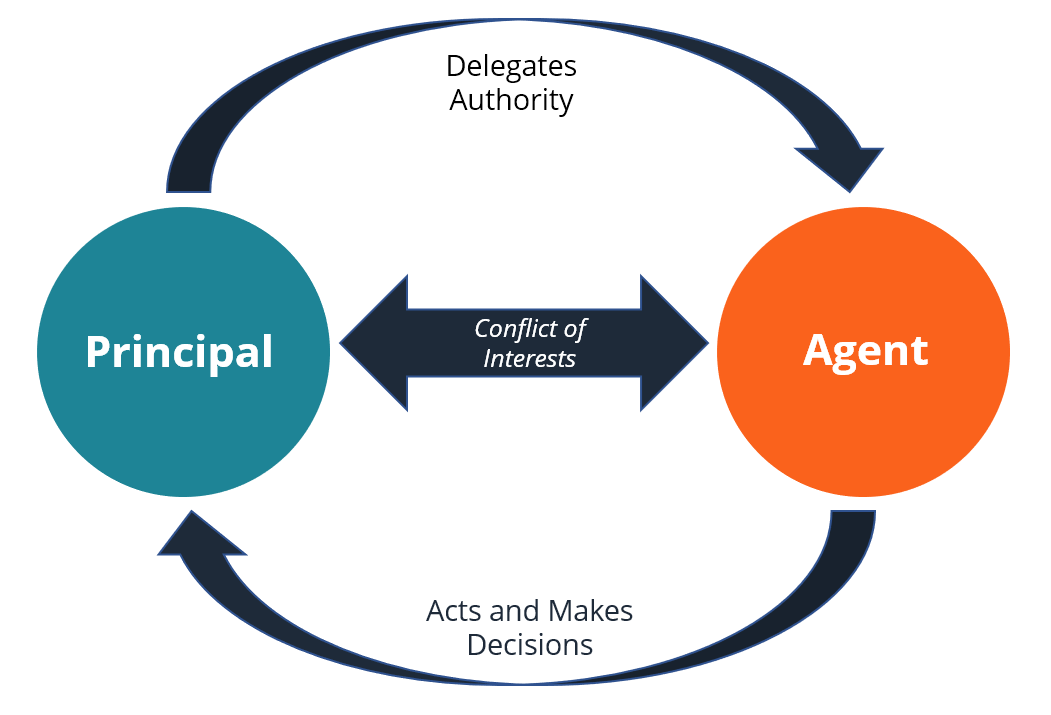
Incentives, Psychology, and Ownership Mindset. Incentives are incredibly powerful in business and its surprisingly difficult to get people to do the right thing. Sleep spends a lot of time on incentives and the so-called Principal-Agent Conflict. Often times the Principal (Owner, Boss, Purchaser, etc.) may employ an Agent (Employee, Contractor, Service) to accomplish something. However the goals and priorities of the principal may not align with that agent. As an example, when your car breaks down and you need to go to a local mechanic to fix it, you (the principal) want to find someone to fix the car as well and as cheaply as possible. However, the agent (the mechanic) may be incentivized to create the biggest bill possible to drive business for their garage. Here we see the potential for misaligned incentives. After 5 years of really strong investment results, Sleep and Zakaria noticed a misaligned incentive of their own: “Which brings me to the subject of the existing performance fee. Eagle-eyed investors will not have failed but notice the near 200 basis point difference between gross and net performance this year, reflecting the performance fee earned. We are in this position because performance for all investors is in excess of 6% per annum compounded. But given historic performance, that may be the case for a very long time. Indeed, we are so far ahead of the hurdle that if the Partnership now earned pass-book rates of return, say 5% per annum, we would continue to “earn” 20% performance fees (1% of assets) for thirty years, that is, until the hurdle caught up with actual results. During those thirty years, which would see me through to retirement, we would have added no value over the money market rates you can earn yourself, but we would still have been paid a “performance fee”. We are only in this position because we have done so well, and one could argue that contractually we have earned the right by dint of performance, but just look at the conflicts!” They could have invested in treasury bonds and collected a performance fee for years to come but they knew that was unfair to limited partners. So the duo created a resetting fee structure, that allowed LPs to claw back performance fees if Nomad did not exceed the 6% hurdle rate for a given year. This kept the pair focused on driving continued strong results through the life of the partnership.
Discovery & Pace. Nick Sleep and Qais Zakaria looked for interesting companies in interesting situations. Their pace is simply astounding: “When Zak and I trawled through the detritus of the stock market these last eighteen months (around a thousand annual reports read and three hundred companies interviewed)…” Sleep and Zakaria put up numbers: 55 annual reports per month (~2 per day), 17 companies interviewed per month (meeting every other day)! That is so much reading. Its partially unsurprising that after a while they started to be able to find things in the annual reports that piqued their interest. Not only did they find retrospectively obvious gems like Amazon and Costco, they also looked all around the world for mispricings and interesting opportunities. One of their successful international investments took place in Zimbabwe, where they noticed significant mispricing involving the Harare Stock Exchange, which opened in 1896 but only started allowing foreign investment in 1993. While Nomad certainly made its name on the Scaled efficiencies shared investment model, Zimbabwe offered Sleep and Zakaria to prioritize their second model: “We have little more than a handful of distinct investment models, which overlap to some extent, and Zimcem is a good example of a second model namely, ‘deep discount to replacement cost with latent pricing power.’” Zimcem was the country’s second-largest cement producer, which traded at a massive discount to replacement cost due to terrible business conditions (inflation growing faster than the price of cement). Not only did Sleep find a weird, mispriced asset, he also employed a unique way of acquiring shares to further increase his margin of safety. “The official exchange rate at the time of writing is Z$9,100 to the U$1. The unofficial, street rate is around Z$17,000 to the U$1. In other words, the Central Bank values its own currency at over twice the price set by the public with the effect that money entering the country via the Central Bank buys approximately half as much as at the street rate. Fortunately, there is an alternative to the Central Bank for foreign investors, which is to purchase Old Mutual shares in Johannesburg, re-register the same shares in Harare and then sell the shares in Harare. This we have done.“ By doing this, Nomad was able to purchase shares at a discounted exchange rate (they would also face the exchange rate on sale, so not entirely increasing the margin of safety). The weird and off the beaten path investments and companies can offer rich rewards to those who are patient. This was the approach Warren Buffett employed early on in his career, until he started focusing on “wonderful businesses” at Charlie Munger’s recommendation.