Psychologist Don Norman takes us through an exploratory journey of the basics in functional design. As the consumerization of software grows, this book’s key principles will become increasingly important.
Tech Themes
Discoverability and Understanding. Discoverability and Understanding are two of the most key principles in design. Discoverability answers the questions of, “Is it possible to figure out what actions are possible and where and how to perform them?” Discoverability is absolutely crucial for first time application users because poor discovery of actions leads to low likelihood of repeat use. In terms of Discoverability, Scott Berkun notes that designers should prioritize what can be discovered easily: “Things that most people do, most often, should be prioritized first. Things that some people do, somewhat often, should come second. Things that few people do, infrequently, should come last.” Understanding answers the questions of: “What does it all mean? How is the product supposed to be used? What do all the different controls and settings mean?” We have all seen and used applications where features and complications dominate the settings and layout of the app. Understanding is simply about allowing the user to make sense of what is going on in the application. Together, Discoverability and Understanding lay the ground work for successful task completion before a user is familiar with an application.
Affordances, Signifiers and Mappings. Affordances represent the set of possible actions that are possible; signifiers communicate the correct action that should take place. If we think about a door, depending on the design, possible affordances could be: push, slide, pull, twist the knob, etc. Signifiers represent the correct action or the action the designer would like you to perform. In the context of a door, a signifier might be a metal plate that makes it obvious that the door must be pushed. Mappings provide straightforward correspondence between two sets of objects. For example, when setting the brightness on an iPhone, swiping up increases brightness and swiping down decreases brightness, as would be expected by a new user. Design issues occur when there is a mismatch in affordances, signifiers and mappings. Doors provide another great example of poor coordination between affordances, signifiers and mappings - everyone has encountered a door with a handle that says push over it. This normally followed by an uncomfortable pushing and pulling motion to discover the actions possible with the door. Why are there handles if I am supposed to push? Good design and alignment between affordances, signifiers and mappings make life easier for everyone.
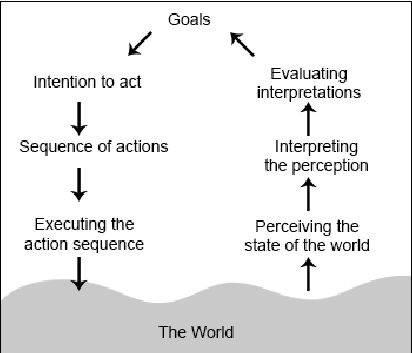
The Seven Stages of Action. Norman lay outs the psychology underpinning user decisions in seven stages - Goal, Plan, Specify, Perform, Perceive, Interpret, Compare. The first three (Goal, Plan, Specify) represent the clarification of an action to be taken on the World. Once the action is Performed, the final three steps (Perceive, Interpret, Compare) are trying to make sense of the new state of the World. The seven stages of action help generalize the typical user’s interactions with the World. With these stages in mind, designers can understand potential breakdowns in discoverability, understanding, affordances, signifiers, and mappings. As users perform actions within applications, understanding each part of the customer journey allows designers to prioritize feature development and discoverability.
Business Themes
The best product does not always win, but... If the best product always won out, large entrenched incumbents across the software ecosystem like IBM, Microsoft, Google, SAP, and Oracle would be much smaller companies. Why are there so many large behemoths that won’t fall? Each company has made deliberate design decisions to reduce the amount of customer churn. While most of the large enterprise software providers suffer from Feature Creep, the product and deployment complexity can often be a deterrent to churn. For example, Enterprise CIOs do not want to spend budget to re-platform from AWS to Azure, unless there was a major incident or continued frustration with ease of use. Interestingly enough though, as we’ve discussed, the transition from license-maintenance software to SaaS, as well as the consumerization of the enterprise, are changing the necessity of good design and user experience. If we look at Oracle for example. The business has made several acquisitions of applications to be built on Oracle Databases. But the poor user experience and complexity of the applications is starting to push Oracle out of businesses.
Shipping products on time and on budget. “The day a product development process starts, it is behind schedule and above budget.” The product design process is often long and complex because there is a wide array of disciplines involved in the process. Each discipline thinks they are the most important part of the process and may have different reasons for including a singular feature, which may conflict with good design. To alleviate some of that complexity, Norman suggests hiring design researchers that are separate from the product development focus. These researchers focus on how users are working in the field and are coming up with additional use cases / designs all the time. When the development process kicks off, target features and functionality have already been suggested.
Why should business leaders care about good design? We have already discussed how product design can act as a deterrent to churn. If processes and applications become integral to Company function, then there is a low chance of churn, unless there is continued frustration with ease of use. Measuring product market fit is difficult but from a metrics perspective; companies can look at gross churn ($ or customer amount that left / beginning ARR or beginning customers) or NPS to judge how well their product is being received. Good design is a direct contributor to improved NPS and better retention. When you complement good design with several hooks into the customers, churn reduces.