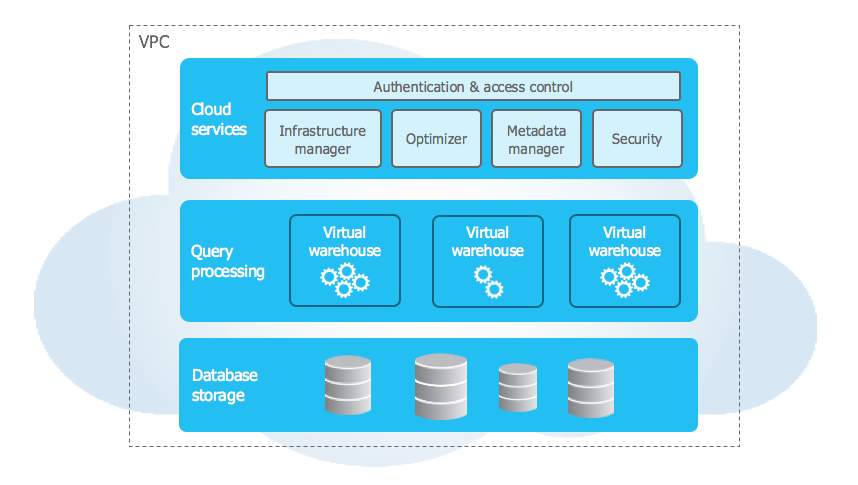
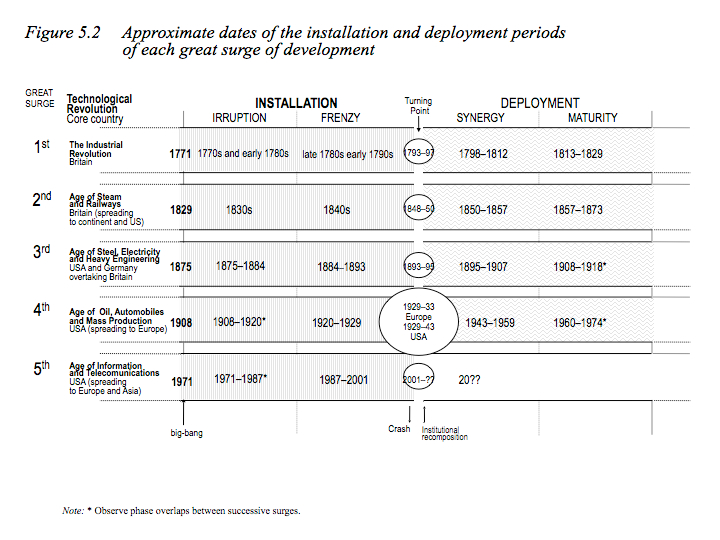
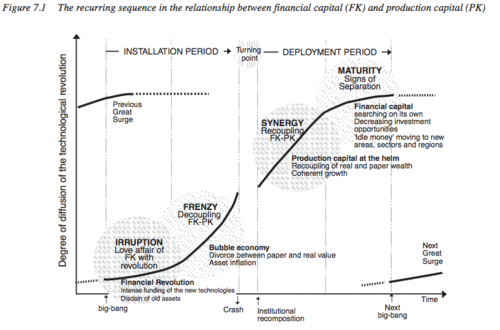
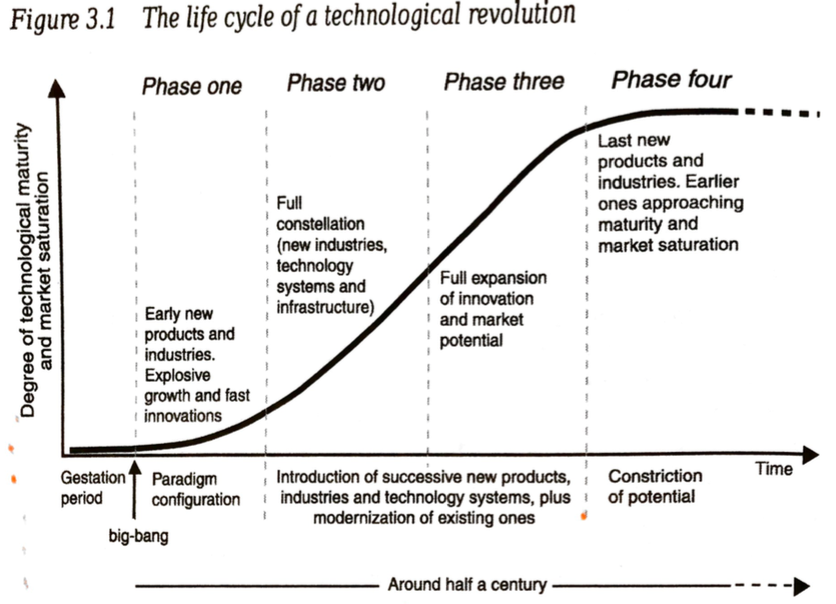
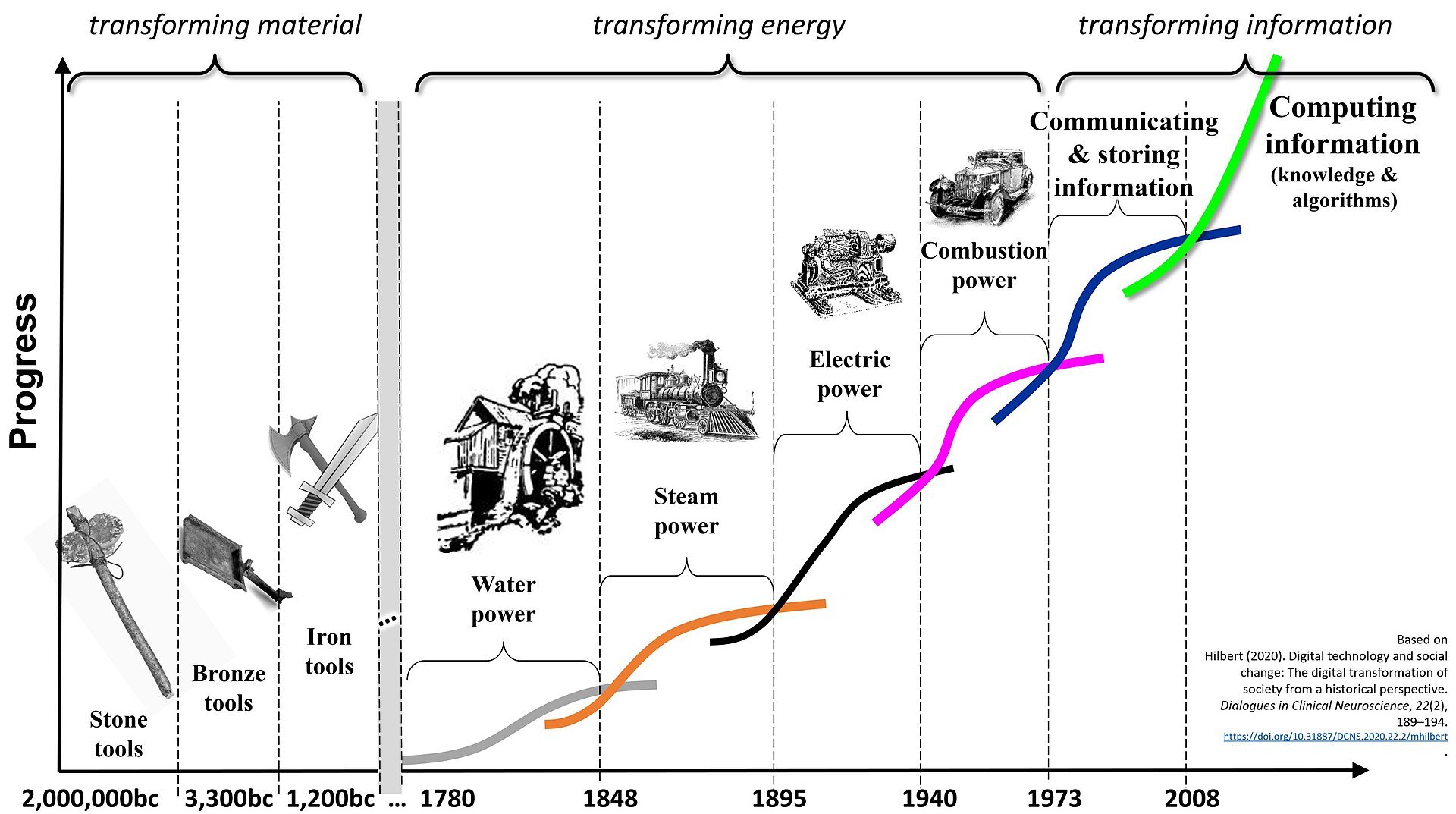
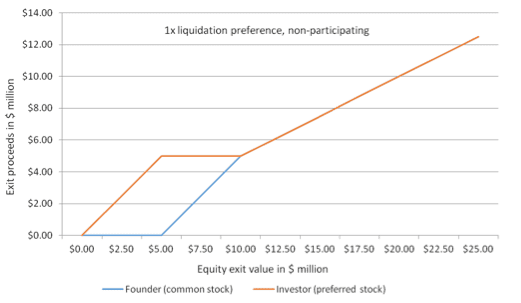
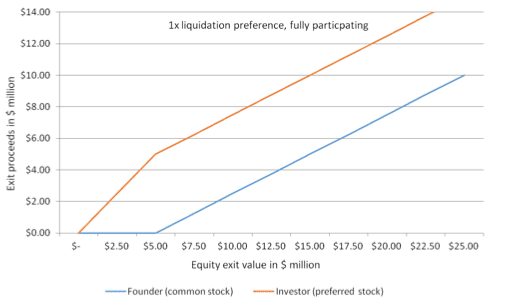
This month we hear the story of famous technology CEO Shellye Archambeau, former leader of GRC software provider, Metricstream. Archambeau packs her memoir full of amazing stories and helpful career advice; the book is a must-read for any ambitious leader looking for how to break into Silicon Valley’s top ranks.
Tech Themes
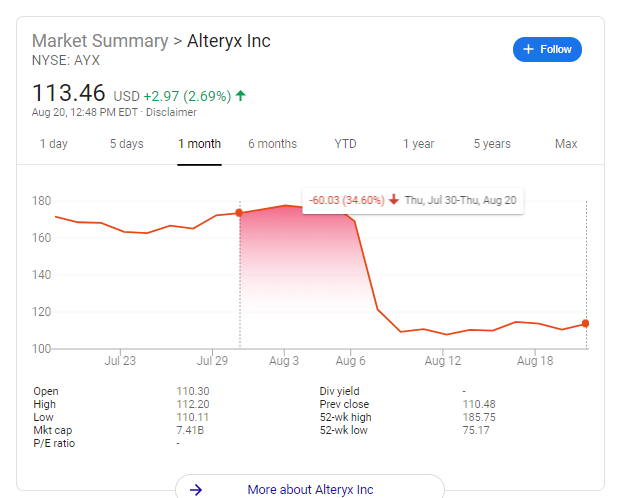
The Art of the Pivot. When Archambeau joined Zaplet in 2003 as its new CEO, she had a frank conversation with the chairman of the board Vinod Khosla. She asked him one question: “You have a great reputation for supporting your companies, but you also have a reputation of being strong-willed and sometimes dominating. I just need to know before I answer [where I will take the job], are you hiring me to implement your strategy, or are you hiring me to be the CEO?” Vinod responded: “I would be hiring you to be the CEO, to run the company, fully responsible and accountable.” With that answer, Archambeau accepted the job and achieved her life-long goal of becoming a CEO before age forty. Archambeau had just inherited a struggling former silicon-valley darling that had raised over $100M but had failed to translate that money into meaningful sales. Zaplet’s highly configurable technology was a vital asset, but the company had not locked on to a real problem. Struggling to set a direction for the company, Archambeau spoke with board member Roger McNamee, who suggested pivoting into compliance software. In early 2004, Zaplet merged with compliance software provider MetricStream (taking its name), with Archambeau at the helm of the combined company. She wasn’t out of the woods yet. The 2008/09 financial crisis pushed MetricStream to the brink. With less than $2M in the bank, Archambeau ditched her salary, executed a layoff, and rallied her executive through the financial crisis. As banks recapitalized, they sought new compliance and risk management platforms to avoid future issues, and MetricStream was well-positioned to serve this new set of highly engaged customers. Archambeau’s first and only CEO role lasted for 14 years, as she led Metricstream to $100M in revenue and 2,000+ employees.
Taking Calculated Risks. Although Archambeau architected a successful turnaround, her career was not without challenges. After years of working her way up at IBM, Archambeau strategically chose to seek out a challenging international assignment, an essential staple of IBM’s CEOs. While working in Tokyo as VP and GM for Public Sector in Asia Pacific, Archambeau was not selected for a meeting with Lou Gerstner, IBM’s CEO. She put it bluntly: “I was ranked highly in terms of my performance - close to the top of the yearly ranking, not just in Japan, but globally. Yet I was pretty sure I wasn’t earning the salary many of my colleagues were getting.” It was then that Archambeau realized that she might need to leave IBM to achieve her goal of becoming CEO. She left IBM and became President of Blockbuster.com, as they were beginning to compete with Netflix. Blockbuster was staunch in its dismissal of Netflix, refusing to buy the streaming company when it had a chance for a measly $50M. Archambeau was unhappy with management’s flippant attitude toward a legitimate threat and left Blockbuster’s Dallas HQ after only 9 months. After this difficult work experience, Archambeau sought out work in Silicon Valley, moving to the nation’s tech hub without her family. She became Head of Sales and Marketing for Northpoint Communications. The company was fighting a losing DSL cable battle, and after a merger with Verizon fell through, the company went bankrupt. Then Archambeau became CMO of Loudcloud, Ben Horowitz’s early cloud product covered in our March 2020 book, The Hard Thing About Hard Things. But things were already blowing up at Loudcloud, and after a year, Archambeau was looking for another role following the sale of LoudCloud’s services business to EDS. At 40 years old, Archambeau had completed international assignments, managed companies across technology, internet, and telecom, and seen several mergers and bankruptcies. That experience laid the bedrock for her attitude: “After the dot-com bubble burst, I would need to double down and take greater risks, but-and this probably won’t surprise you-I had planned for this…It’s 2002, I’m almost forty, I’ve learned a great deal from Northpoint and Loudcloud, and I’m feeling ready for my chance to be a CEO.” Archambeau was always ready for the next challenge, unafraid of the risks posed - prepared to make her mark on the Tech industry.
Find the Current. Trends drive the Tech industry, and finding and riding those trends can be hugely important to creating a career. As in Archambeau’s journey, she saw the growing role of technology as an intern at IBM in the 1980s and knew the industry would thrive over time. As the internet and telecom took hold, she jumped into new and emerging businesses, unafraid of roadblocks. As she puts it: “Ultimately, when it comes to reaching your goals, the real skill lies in spotting the strongest current - in an organization, in an industry, even in the larger economy - and then positioning yourself so it propels you forward. Sail past the opportunities that lead you into the weeds and take the opportunities that will move you toward your goals.”
Business Themes
The Power of Networking. One of Archambeau’s not-so-secret strategies toward career success was networking. She is a people person and radiates energy in every conversation. Beyond this natural disposition, Archambeau took a very concerted and intentional approach toward building her network, and it shows. Archambeau crosses paths with Silicon Valley legends like Bill Campbell and Ben Horowitz throughout the book. Beyond one-to-one mentorship relationships, Archambeau joined several organizations to grow her network, including Watermark, the Committee of 200, ITSM Form, Silicon Valley Leadership Group, and more. These groups offered a robust foundation and became a strong community, empowering and inspiring her to lead!
Support and Tradeoffs. As a young college sophomore, Archambeau knew she wanted to be the breadwinner of the family. When she met her soon-to-be husband Scotty, a 38-year-old former NFL athlete, she was direct with him: “I would really like to be able to have someone stay home with the kids, especially when they are in school. But the thing is…I just don’t want it to be me.” Scotty thought patiently, “You know, Archambeau, I’ve had a lot of experiences in my life. I’ve had three different careers and you know I like working. But, I think I could see myself doing that, for you.” That was the icing on top of the cake. The two married and had two children while Archambeau worked up the ranks to become CEO. Scotty took care of the kids, Kethlyn and Kheaton, when Archambeau moved to Silicon Valley for work. She understood the tough tradeoff she was making and acknowledged that her relationship with her daughter felt more strained during Kethlyn’s teenage years. It begs the question, how comfortable are you with the tradeoffs you are making today? Moving to a new city to pursue a career that may strain family dynamics is never an easy decision. Family was always important to Archambeau, but it became front and center when Scotty was diagnosed with blood cancer in 2010. Although she was still CEO of MetricStream, things changed: “I had accumulated vacation days, I was putting off trips and experiences for ‘when the time was right’…We’re going to do things that we would have waited to do. We’re going to them now.” Family and friends became a priority - they always were!
Earning Respect. As a Black woman in Technology, Archambeau had to overcome the odds repeatedly. She recounted: “As a young African American woman, I was accustomed to earning respect. Whenever I got a promotion or a new job, I walked into it understanding that people likely would assume I was not quite qualified or not equity ready. I presumed I need to establish relationships and credibility, to develop a reputation, to prove myself.” While incredibly sad that Archambeau had to deal with this questioning, she learned how to use it to her advantage. As her family moved around the country, Archambeau faced repeated challenges: getting denied from taking advanced classes in school, getting bullied and beaten walking home from school, and starting high school with leg braces in a new city. Through these difficulties, she developed a simple methodology for getting through tough times: “Accept the circumstances, fake it ‘til you make it, control what you can, and trust that things will get better.” Archambeau took that mentality with her and earned the respect of the entire IBM Japan when she presented her introduction slides entirely in Japanese to build trust with her new co-workers. It was the first time a foreign executive had done so. Archambeau’s ability to boldly take action in face of many obstacles is impressive.